Monte Carlo uncertainty propagation for ESA SCOPE.
Installing and testing
Read INSTALL.md for detailed instructions on installation and testing.
Operations Manual
Operational principles
Processors are coded in Python and require an environment described
in INSTALL.md. The kaleidoscope directory
includes the kaleidoscope Python package, which includes the Kaleidoscope
processors. The processors are invoked from the command line. Typing
kaleidoscope-scatter --help
kaleidoscope-collect --help
will print a detailed usage messages to the screen, like
usage: kaleidoscope-scatter [-h] --source-type
{esa-cci-oc,esa-scope-cs,esa-scope-pp,ghrsst,glorys}
--selector {0,1,2,...,100}
[--antithetic]
[--engine-reader {h5netcdf,netcdf4,zarr}]
[--engine-writer {h5netcdf,netcdf4,zarr}]
[--log-level {debug,info,warning,error,off}]
[--mode {multithreading,synchronous}]
[--workers {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8}] [--progress]
[--stack-traces] [-v]
source_file target_file
This scientific processor produces a Monte Carlo ensemble from given
uncertainties.
positional arguments:
source_file the file path of the source dataset.
target_file the file path of the target dataset.
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--source-type {esa-cci-oc,esa-scope-cs,esa-scope-pp,ghrsst,glorys}
the source type. (default: None)
--selector {0,1,2,...,100}
the Monte Carlo stream selector. An integral number
which must not be negative. (default: None)
--antithetic enable pairwise antithetic Monte Carlo simulation.
(default: False)
--engine-reader {h5netcdf,netcdf4,zarr}
specify the engine used to read the source product
file. (default: None)
--engine-writer {h5netcdf,netcdf4,zarr}
specify the engine used to write the target product
file. (default: None)
--log-level {debug,info,warning,error,off}
specify the log level. (default: None)
--mode {multithreading,synchronous}
specify the operating mode. In multithreading mode a
multithreading scheduler is used. In synchronous mode
a single-thread scheduler is used. (default: None)
--workers {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8}
specify the number of workers used in multithreading
mode. If not set, the number of workers is determined
by the system. (default: None)
--progress enable progress bar display. (default: False)
--stack-traces enable Python stack traces. (default: False)
-v, --version show program's version number and exit
Copyright (c) Brockmann Consult GmbH, 2025. License: MIT
and
usage: kaleidoscope-collect [-h] --source-type
{esa-scope-dic,esa-scope-doc,esa-scope-pc,esa-scope-pic,esa-scope-poc,esa-scope-pp}
[--engine-reader {h5netcdf,netcdf4,zarr}]
[--engine-writer {h5netcdf,netcdf4,zarr}]
[--log-level {debug,info,warning,error,off}]
[--mode {multithreading,synchronous}]
[--workers {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8}] [--progress]
[--stack-traces] [-v]
source_glob target_file
This scientific processor computes standard uncertainty from a given Monte
Carlo ensemble.
positional arguments:
source_glob the file path glob of the source datasets. The first
entry in the expanded list of file paths shall refer
to the nominal (i.e., not randomized) source dataset.
The remaining entries shall refer to randomized
variants of the nominal source. Only the '*' character
shall be used for globbing.
target_file the file path of the target dataset.
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--source-type {esa-scope-dic,esa-scope-doc,esa-scope-pc,esa-scope-pic,esa-scope-poc,esa-scope-pp}
the source type. (default: None)
--engine-reader {h5netcdf,netcdf4,zarr}
specify the engine used to read the source product
file. (default: None)
--engine-writer {h5netcdf,netcdf4,zarr}
specify the engine used to write the target product
file. (default: None)
--log-level {debug,info,warning,error,off}
specify the log level. (default: None)
--mode {multithreading,synchronous}
specify the operating mode. In multithreading mode a
multithreading scheduler is used. In synchronous mode
a single-thread scheduler is used. (default: None)
--workers {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8}
specify the number of workers used in multithreading
mode. If not set, the number of workers is determined
by the system. (default: None)
--progress enable progress bar display. (default: False)
--stack-traces enable Python stack traces. (default: False)
-v, --version show program's version number and exit
Copyright (c) Brockmann Consult GmbH, 2025. License: MIT
Normal operations
To invoke the processor from the terminal, for instance, type
kaleidoscope-scatter --source-type ghrsst --selector 17 in.nc out.nc
which normally will log information to the terminal, e.g.,
2025-05-22T08:29:19.999000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] starting running processor
2025-05-22T08:29:19.999000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] config: engine_reader = None
2025-05-22T08:29:19.999000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] config: engine_writer = None
2025-05-22T08:29:19.999000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] config: log_level = info
2025-05-22T08:29:19.999000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] config: mode = multithreading
2025-05-22T08:29:19.999000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] config: processor_name = kaleidoscope-scatter
2025-05-22T08:29:19.999000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] config: processor_version = 2025.1.1
2025-05-22T08:29:19.999000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] config: progress = False
2025-05-22T08:29:19.999000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] config: selector = 17
2025-05-22T08:29:19.999000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] config: source_file = in.nc
2025-05-22T08:29:19.999000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] config: source_type = ghrsst
2025-05-22T08:29:19.999000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] config: stack_traces = False
2025-05-22T08:29:19.999000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] config: target_file = out.nc
2025-05-22T08:29:19.999000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] config: tmpdir = .
2025-05-22T08:29:19.999000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] config: workers = 2
2025-05-22T08:29:20.108000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] starting creating processing graph
2025-05-22T08:29:20.110000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] starting graph for variable: analysed_sst
2025-05-22T08:29:23.228000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] finished graph for variable: analysed_sst
2025-05-22T08:29:23.228000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] finished creating processing graph
2025-05-22T08:29:23.228000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] starting writing target dataset: out.nc
2025-05-22T08:29:29.476000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] finished writing target dataset
2025-05-22T08:29:29.476000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] starting closing datasets
2025-05-22T08:29:29.477000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] finished closing datasets
2025-05-22T08:29:29.477000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] finished running processor
2025-05-22T08:29:29.477000Z <node> kaleidoscope-scatter 2025.2.0 [71491] [I] elapsed time (seconds): 9.478
and eventually produce a randomized output dataset. Normally, the processor
will terminate with an exit code of 0.
Error conditions
The processor terminates on the first occurrence of an error. The exit code
of the processor is 0 if the processor completed without errors, and nonzero
otherwise. Warning and error messages are sent to the standard error stream.
Recovery operations
There are no recovery operations.
Expected output
Scatter
Kaleidoscope Scatter generates Monte Carlo variants of source data which exhibit simulated errors. At present, only uncorrelated random errors are simulated. Normalized errors will have a mean value of zero and a standard deviation of unity, with statistical deviations implied by constraints on the error probability distribution and the (limited) number of variants generated.
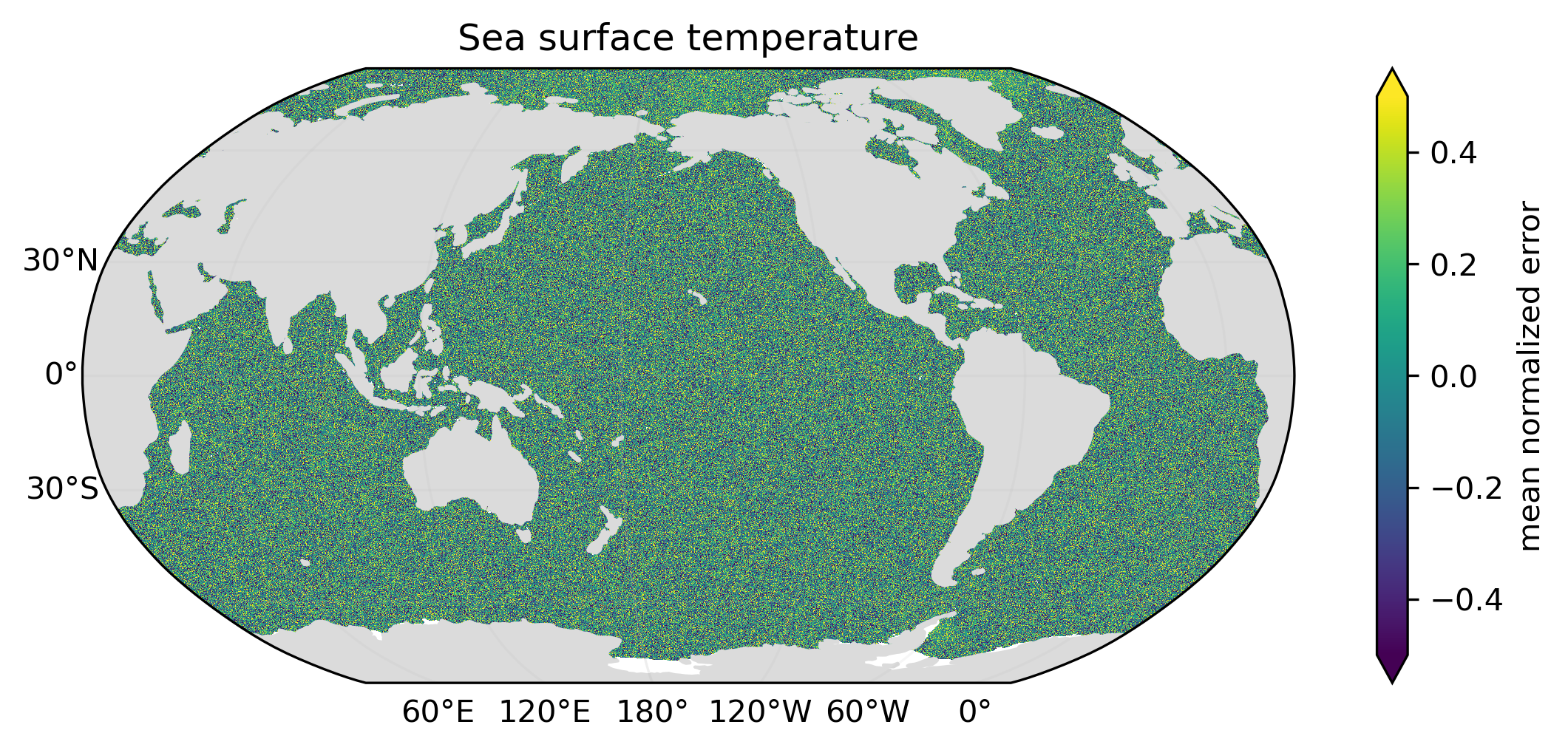
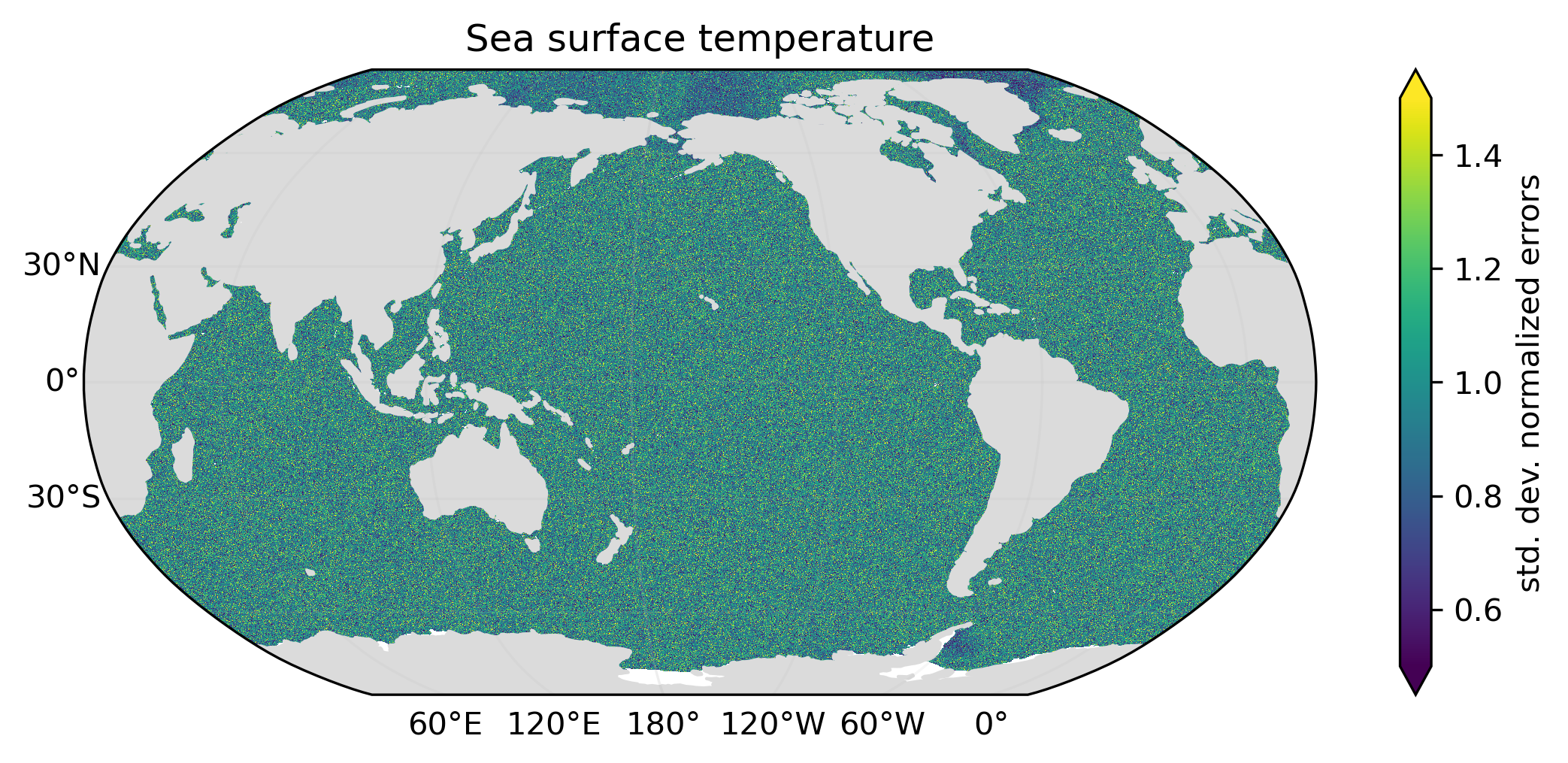
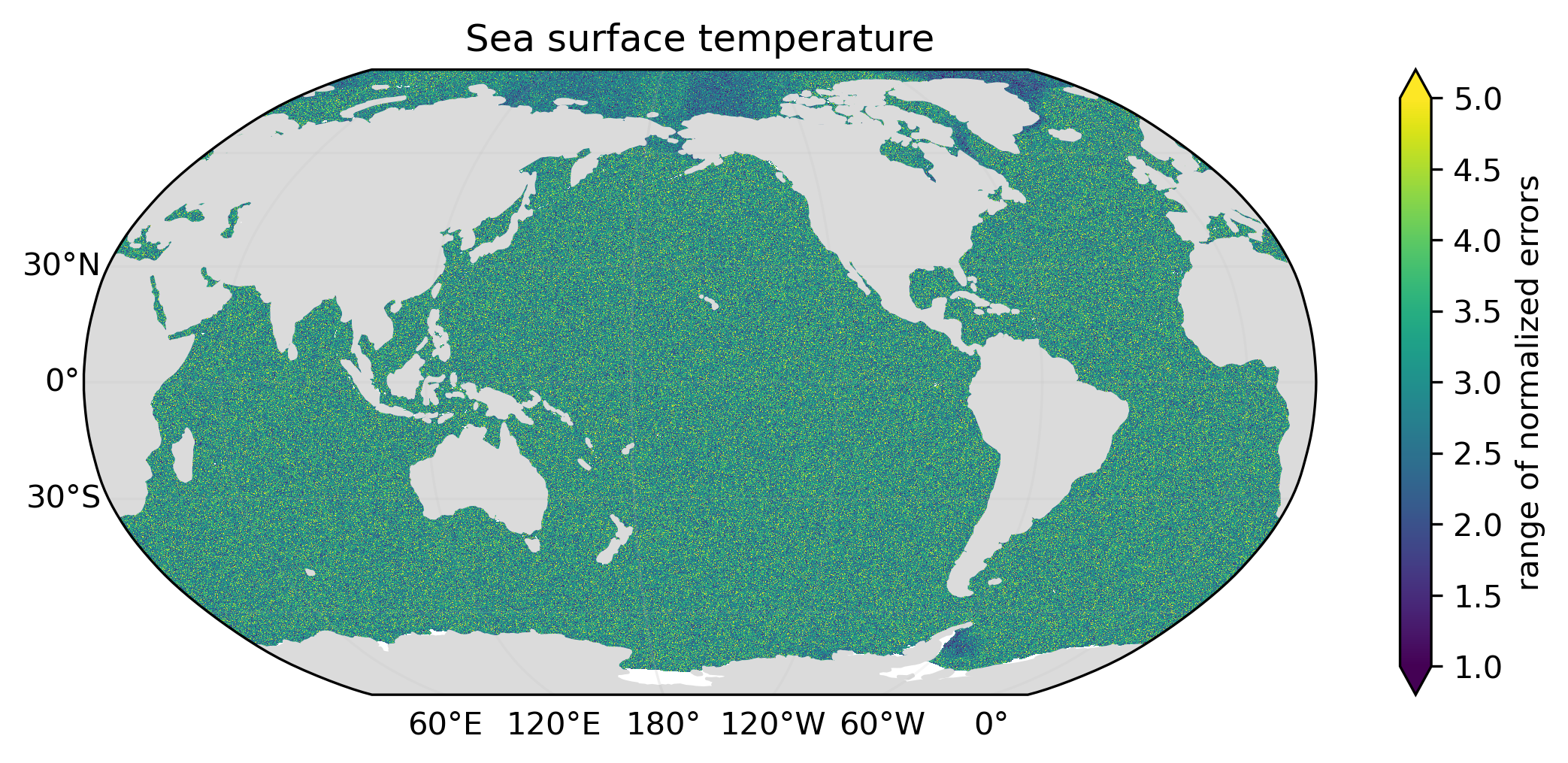
Examples above illustrate the mean, the standard deviation and the minimum-to-maximum range of normalized simulated errors for an ensemble of ten variants of global monthly sea surface temperature (January 2000). The standard deviation and range of normalized errors is reduced at the North Pole and in the Weddell Sea due to constraints imposed by the freezing point of seawater.
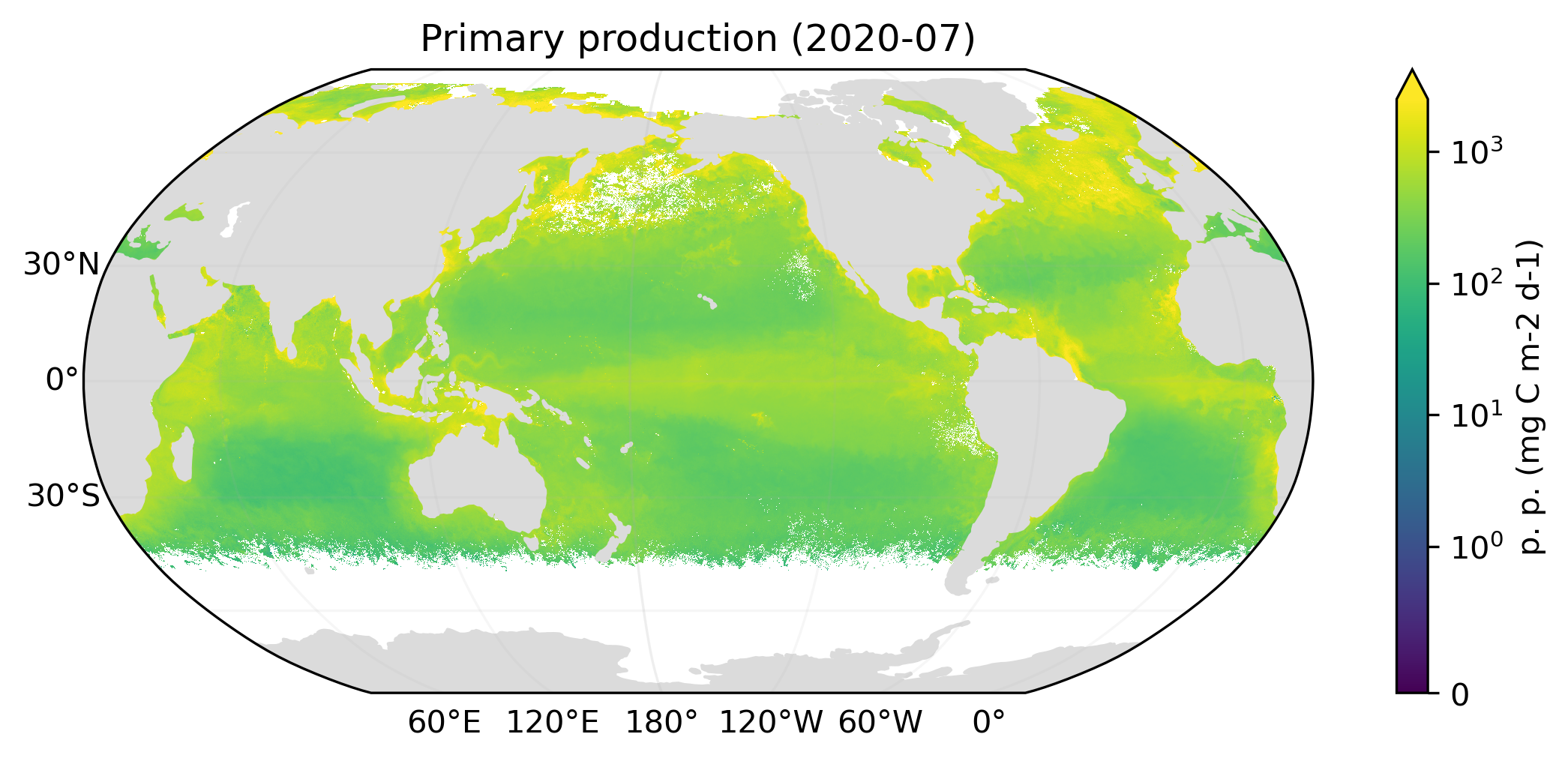
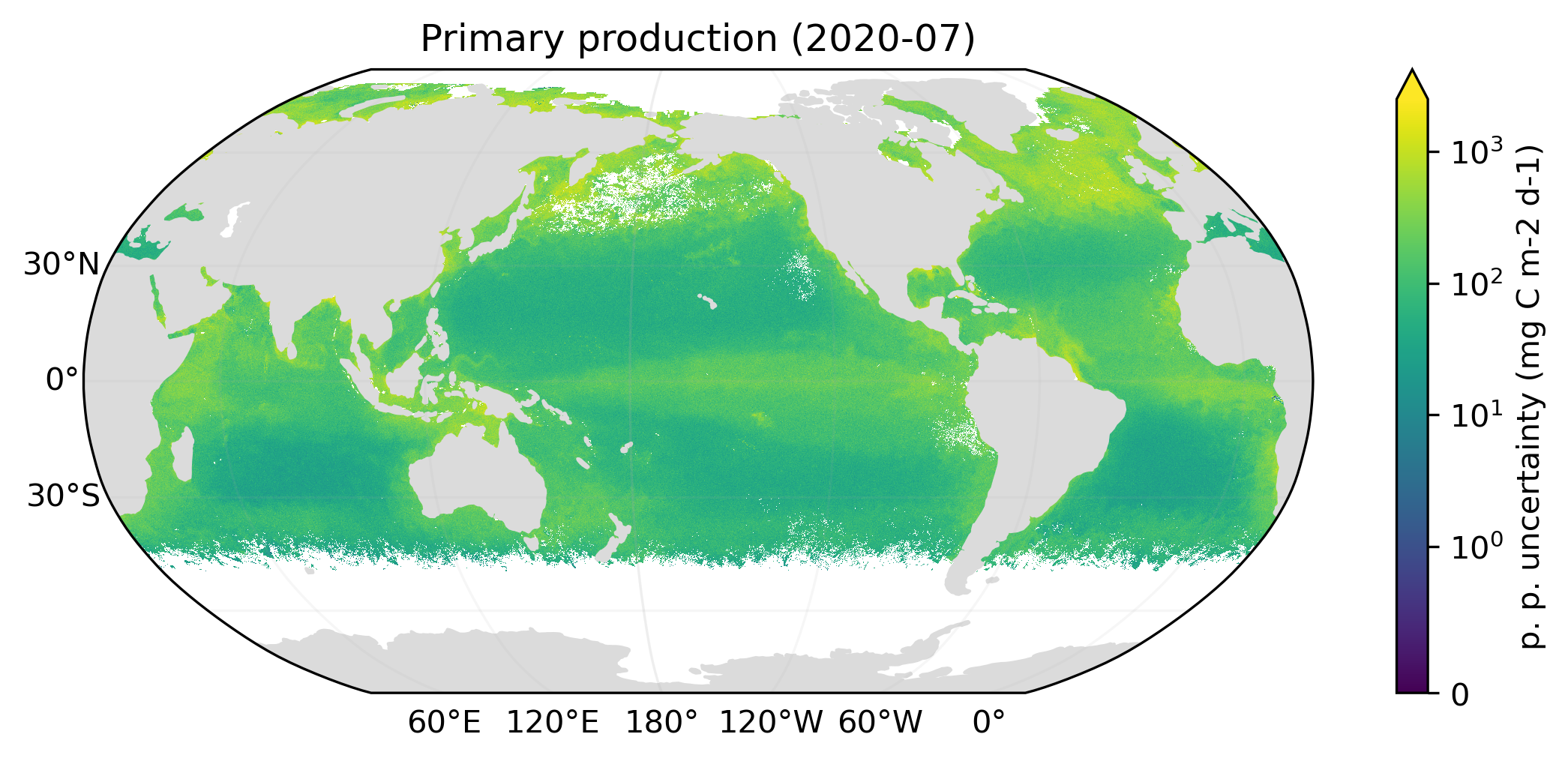
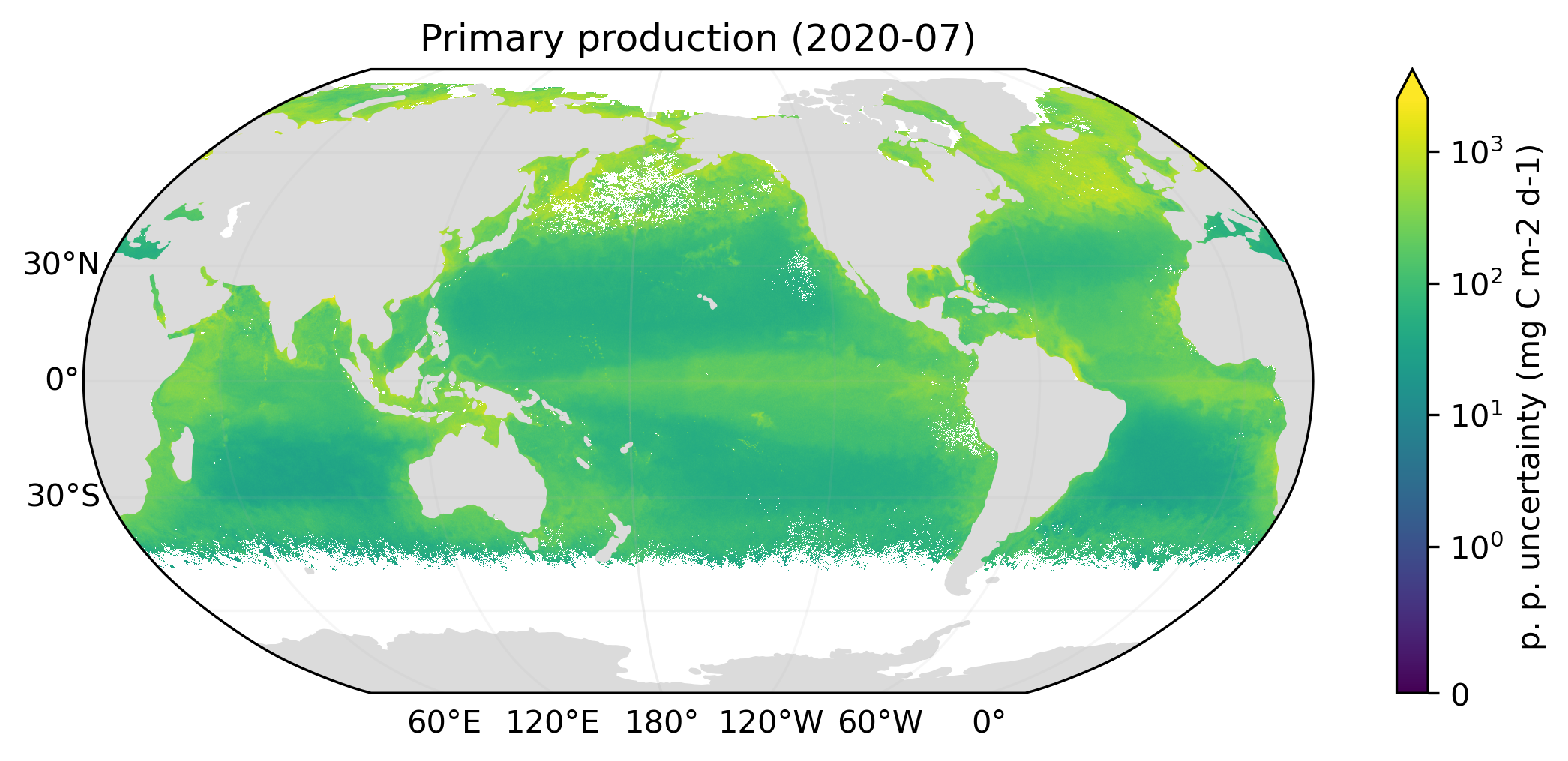
Collect
Kaleidoscope Collect generates standard uncertainty from Monte Carlo variants. Examples below illustrate the nominal primary production and its uncertainty. Standard uncertainty typically exhibits statistical fluctuation, which is an artifact of the Monte Carlo method. Therefore, a low-pass filtered standard uncertainty is produced in addition.